Published On: Feb 13, 2015
Proper electricity supply is a catalyst and vital input for the sustenance and inclusive growth of all. This growth largely depends on availability of reliable and quality electric supply. Reliability and Quality of power are important for all concerned and many times the terms are considered synonymous (which is not the case in real scenario). Reliability and Quality have their own characteristics. While there are already various reliability parameters being measured, however there are hardly any clear measurement of power quality or its impact on business and life. Poor power quality has become crucial for distribution utilities and high-end customers/industries worldwide (including India).
Power Quality (PQ) is a real concept and not a utopian one. In Indian scenario, there is an urgent need to create awareness and implement appropriate programs for PQ mitigation. From our earlier blog, Are Developing Economies At Risk Due To Power Quality Issues And Challenges, it can be observed that there are significant techno-economic consequences for concerned stakeholders especially end customers due to poor PQ. In practice, power quality is not just a single term but rather encompasses a cluster of issues across the power distribution value chain. PQ not only impacts distribution utilities or high-end industries but also household consumers. Variations in supply frequency, voltage, current, voltage dip, flicker, short & long interruptions and harmonics are all different types of PQ issues.
All above-mentioned issues make PQ important and need for its immediate awareness and implementation. This blog showcases the key barriers and some potential best practices for scale-up and implementation of Power Quality improvement programs (PQP).
KEY BARRIERS IN PQ IMPLEMENTATION IN INDIA AND WORLDWIDE
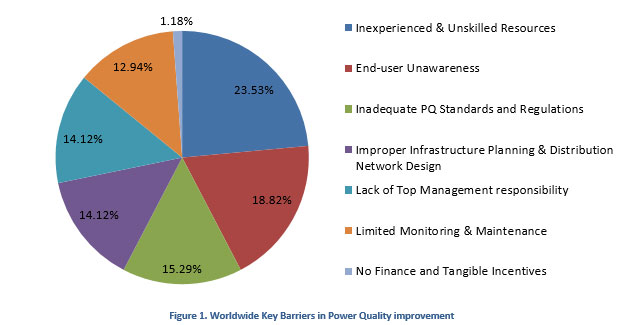
As per one of the research study conducted by International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, in April-2012, following key barriers were reported in scaling-up of PQ implementation. (This research study also includes key barriers faced by India, which is almost similar to Worldwide barriers)
It can be observed from the above chart that Inexperienced & Unskilled Resources form the main barrier faced by many countries including that of USA, UK, Australia, European, African and Asian Countries. This is followed by End-user Awareness, which is faced by many African, Asian and European countries (except Germany and Netherlands). These two barriers constitute a consideration 45% worldwide. Others like Standards & Regulations, Network Design, No/Limited PQ Monitoring, etc. comprise the remaining share.
Financing and Incentives are considered to be the lowest barriers in PQ implementation; hence it is quite evident that the major reasons for PQ improvement are mainly due to its unawareness, improper planning and monitoring and not only because of financial constraint. Before we discuss some potential ways of eliminating these barriers, let’s develop a brief understanding about them:
- Inexperienced & Unskilled Resources: At one point, utilities are being ignorant about PQ & its associated issues. Further due to lack of experience and resources they add to PQ woes in electricity network. Inexperience of utility staff poses a major challenge for PQ mitigation for most utilities.
- End-user Unawareness: The complex mix of end-users such as industrial, commercial and residential customers connected to distribution network makes PQ issue more complex as each of them induces certain harmonics back into the electrical network system. Awareness among these end-users regarding PQ is highly missing, which is another major challenge. Besides sensitivity of end users towards poor PQ varies widely based on their dependence on electricity.
- Inadequate PQ Standards & Regulations: Although various utilities have well-developed Grid (Transmission level) regulation at transmission voltage levels, however there is weak or no standard for key PQ related issues like Flickers, Voltage dips, Interruptions and current harmonics. This is more so when it comes to distribution level. Such inadequacy of PQ Standards and Regulations needs focused and immediate intervention at regulatory level.
- Improper Infrastructure Planning & Distribution Network design: With the ever-increasing need of meeting the growing power requirement, the existing network systems are unable to cater to the current demand of power quality and grid reliability. To add to that, poor designs of systems and poor selection of power electronics driven equipment by high-end industries are frequently encountered with PQ related issues. It is important that the utilities and end users recognize the need to overcome PQ issues by proper planning and upgrading the network or equipment system with available technology interventions and practices.
- Lack of Top Management responsibility: Poor PQ also arises from end-users power utilization (in addition to utility’s network) and has a direct impact on their internal & external power systems too. Generally, top management of industries does not recognize PQ as an issue rather downplays it as O&M issue causing significant economic loss. Implementation of any program related to power quality requires considerable attention from top management to improve the distribution networks. However, lack or absence of clearly defined specific PQ parameters and its data makes it even more difficult for the management to take a decision. Economic dimension is dormant since it doesn’t reflect in increasing output due to ignorance.
- Limited Monitoring & Measurements: Limited or no proper power quality monitoring & measurement makes it difficult for utilities and end-users to assess the economic impacts due to poor PQ and hence its implementation takes a hammering. This is one of the critical barriers for PQ improvement. It goes in line with the saying that, ‘What you don’t measure, you cannot manage’.
- No Finance & Tangible Incentives: Lack of financial sources for network revamping and infrastructure development is another barrier for PQ improvement in utilities. Similarly, unlike power factor improvement wherein an incentive/disincentive is associated, their are no tangible incentives & subsidies to end-consumers for maintaining power quality levels, as they do not directly affect billing always. For industry, PQ mitigation pays for itself if impact is rightly measured and assessed.
BEST PRACTICES TO ELIMINATE PQ BARRIERS IN INDIA
Utilities in India should learn from their progressive counterparts in India & abroad and implement Power Quality Program (PQP) to eliminate the barriers for improving PQ. Effective implementation of PQP will definitely yield positive and substantial benefits. Implementing a right PQ approach is a collective effort by all stakeholders, i.e. from field team to engineers to top management. Some of the best practices that should be followed for implementing PQP includes:
- Management Commitment: is of utmost importance for PQ improvement. Management practices such as associated management planning, long-term strategy and a high level of employee experience are very significant factors in solving PQ problems. There should be no obstacle in obtaining and collecting PQ data to diagnose the problems, followed by adequate and comprehensive system for solving them. Management should be committed and be able to solve any PQ problems in the system.
- Distribution Network Design: Infrastructure is generally the main reason for major PQ problems for utilities, which has not been upgraded with ever increasing demand. Utilities should upgrade and design the network in order to accommodate the market and new technological innovations. The utilities should upgrade and design the distribution networks “holistically”, on the basis of the existing level of demand for both consumers and power supplies. For industries, the major causes of PQ issu es, besides voltage quality received from DISCOMs, are poor selection of power electronics and other electronic equipment. Generally, unbalanced systems, poor earthing, electric motors and other sensitive equipment like variable speed drive, computers, etc. forms substantial part of PQ issues in the industry. A detailed study of network should be carried out and proper management planning should be made in solving technical problems. A significant investment should be made for network up gradation and allied activities.
- Power Quality (PQ) Database: To tackle PQ problem, a foolproof and complete database is essential, as the demand for electricity and electronic devices has increased. PQ databases can be used to provide the equipment specifications and guidelines, identifying which are the most susceptible to PQ variations and informing manufacturers accordingly. Moreover, the database can also be used for accurately analyzing the causes of recorded disturbance and finding appropriate solutions based on set PQ standards. Both awareness and experience are required to analyze the data in order to tackle PQ problems, which can be achieved by running regular training courses in a ways to deal with dataset requirement.
- Power Quality (PQ) Awareness: PQ awareness among utilities and end-users is the key challenge in implementation of PQP. End-users and utilities should be made aware of economic losses related with poor PQ by conducting sessions on PQ. Distributing literature regarding technical and economic know how regarding poor PQ in simple language will help end-users to understand the concept and act accordingly to improve PQ from their side.
- Customer Cooperation: The customers such as agricultural, industrial, commercial and residential induce some harmonics in the system from their side. Such customers should be made aware of harmonics affecting PQ by taking up customer education camps. Co-operation should be taken from these customers by convincing them to install PQ instruments and mitigation measures either on their cost or on utility cost.
- Staff Training: Unskilled and inexperienced employees are one of the weak links in remedying PQ disturbances. Utilities and end-users should run technical training programs continuously to give enough training and knowledge to its employees. Training will encourage employees to find specific techniques for resolving PQ issues across the power systems. Educating the staff and engineers through workshops and seminars is crucial; such activities should promote familiarity with PQ definitions and disturbances. This would raise the awareness level, which would support the attempts of the distribution companies to achieve high levels of PQ performance. Similar effort at industry level can only improve their level of safety, productivity and energy utilization efficiency.
CONCLUSION
With the continuous and ever increasing cost of poor PQ, it is important to adopt a holistic approach for PQ mitigation rather than aiming purely for short-term return outlook. Lack of awareness about PQ impact is one of the basic challenges in implementing PQ measures and hence importance of addressing poor PQ is getting undermined. Understanding PQ by unlearning / relearning the economics of poor PQ is the first step preparing towards a productive/energy efficient economy.
REFERENCES
- Critical Factors Facing Implementation of Power Quality Program – S.S. Sultan, M.K. Darwish International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 4, April-2012
- Power Quality Program Awareness : Framework for Developing Countries – Saad Saleh Sultan Brunel University, London, UK, May-2013
- Power Quality Concerns for Developing Economy – Mr. Manas Kundu, Power Today, July-2013