Published On: Apr 25, 2019
An assessment of how better PQ management in facilities that use Intelligent Building Management Systems (IBMS) leads to improved energy efficiency, reliability, safety of electrical network and satisfaction for the end users.
INTRODUCTION
Buoyed by low costs of automation and a greater need to centralise the controls of the building’s systems, the building automation today is not limited to critical facilities such as hospitals or data centers but increasingly adopted by even commercial or high-end residential buildings. With that, a significant number of buildings are moving up to the next orbital – adding intelligence to the systems. But as buildings get intelligent, the risks to reliability and safety continue to surface and pose threat to business continuity and human life.
Recent examples of various instances in facilities using high-end IBMS where reliability and safety were put to risk due to electrical fault in the network :
- Fire breaks out at a leading mall in crowded urban area in Mumbai
- Fire breaks out from electrical panels at a leading hotel in Mumbai
- Short circuit leads to Fire at a Hospital in Noida
- Last year, sealing the electrical ducts with combustible material led to a fire in a posh residential society killing 4 and injuring several others
- The short circuit in the air conditioning system of a heritage building that houses the Head Quarters of one of India’s biggest business houses led to 3 deaths
- Few years ago, overheating in transformers caused a Fire at one of the most prestigious business parks in Mumbai had led to disruption of services of a India’s then largest mobile service provider
- Few years ago, the tripping of one of the transformers and eventual failure of the UPS System at the posh terminal of India’s leading International Airport led to service disruption for several hours. The incident happened within a few months after it’s inauguration.
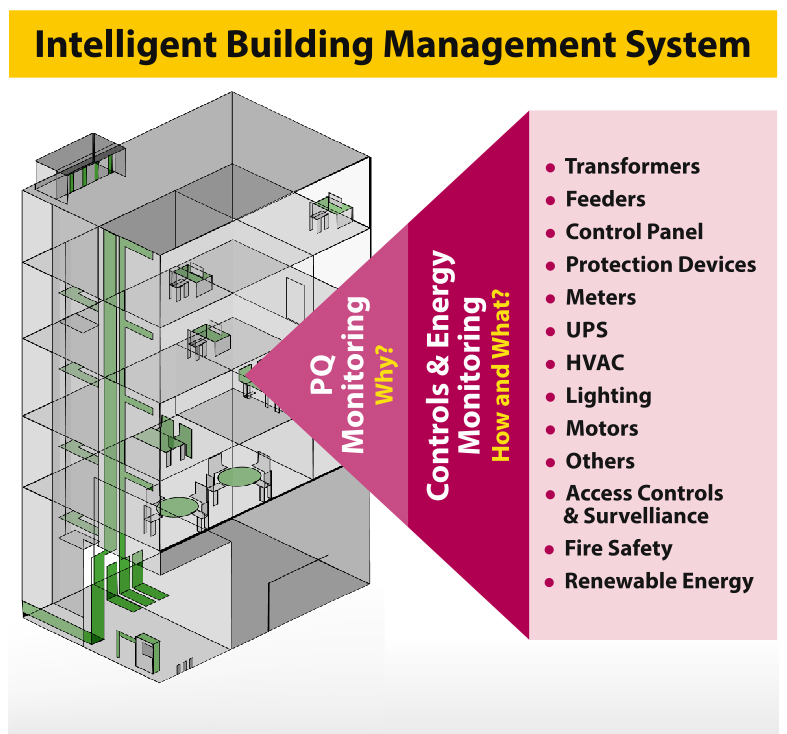
Traditionally, the focus of BMS has been to control and monitor the heating and cooling systems in the building. With greater electronics, the modern IBMS are also controlling the lighting systems and physical access. The IBMS goes a step ahead and offers automation of data acquisition as well as the controls of various systems. Thanks to the IBMS Dashboards, energy consumption in buildings is also being tracked accurately to identify and implement measures to improve energy efficiency. While the IBMS provides building owners and facility managers with a comprehensive view of the mechanical system, it also has the potential to generate significant insights to monitor the electrical systems, especially to improve reliability and safety. Integration of Power Quality (PQ) monitoring in IBMS can show the way.
THE CASE FOR PQ MONITORING IN IBMS
The IBMS dashboards monitors and analyses the energy consumed, mostly using main meter as well as by deploying sub-meters at the load. While this information helps to spot a problem, it is rarely useful in resolving the same. Take for instance, if it is observed that the energy drawn by the Elevator motors is significantly higher than usual, the facility manager comes to know about it through a IBMS dashboard. However, to find the root cause of the fault, he has to wait until the maintenance team has visited the site. Even at this stage, the team may only be able to spot the issue unless it’s a mechanical problem. Integrated PQ monitoring could be of immense help to spot the problem and thus avoid unnecessary repairs or maintenance to find fix the issue.
The reliable and safe operation of the equipment are directly dependent on the quality of power being fed for either control or output delivery. Fluctuation in energy consumption, failures of systems, irrational behaviour of critical assets etc., which are typically monitored by the IBMS, could just be a symptom. Measurement and monitoring of PQ parameters will provide much faster, accurate information for decision making pertaining to reliability of the electrical network.
HOW PQ MONITORING ENHANCES IBMS GOALS
IBMS is concerned about monitoring of individual systems – whether its HVAC, access controls or sensor-controlled lighting. The focus to ensure and update on its functioning, with added observations on the energy usage. The intelligence is applied in automating the changes to equipment under the IBMS based on predefined inputs. The IBMS does not concern itself about how the electrical network as a whole is functioning. Moreover, the focus is not observing how the behaviour of one equipment affects the others or the electrical network. That’s the starting point for Power Monitoring, specifically the PQ parameters.
| IBMS Goals | Added Value by PQ Monitoring |
|---|---|
| How much power is being used? | How the power, being consumed, is used? |
| Is the power use abnormal? | What does the abnormal power use signify? |
| What is the utility billing? | What is the utility billing incurred due to PQ issues? |
| What’s the difference between consumption of energy for similar facilities/equipment? | Why similar facilities/equipment could have a difference in energy consumption? |
PQ monitoring goes beyond just the monitoring of individual equipment functioning or energy consumption and tries to understand how it is affected. Continual PQ monitoring systems integrated with BMS helps to improve energy efficiency by offering the visibility for real-time properties of a building’s electrical supply. The PQ monitoring adds value in a wide range – starting from reducing the energy wastage (arising from poor PQ) to enabling quick identification and resolution of problems to reduce the energy wastage.
However, the difference could most likely be due to these equipment operating in different electrical networks. While IBMS will help to spot the magnitude of difference, an integrated PQ monitoring will help to unfold much deeper insights and thus bring in huge savings in energy consumption, greater uptime of equipment and more.
Tracking power issues leads to longer equipment life and lesser downtime
Aided with IBMS, continuous PQ monitoring can be leveraged to track power issues such as unbalance supply, transients and under/over voltage which typically have a harmful effect on the functioning of critical assets or equipment such as HVAC, Motors, Lighting etc. A large LED lighting load can create significant transients due to its non-linear nature without any change in its energy consumption or functioning. This could lead to wasted power due to distortion and eventually in extreme cases even an electrical network breakdown. PQ monitoring enables the IBMS to prevent such damage and possibility of the downtime can be minimised.
Monitoring PQ parameters helps to arrest capacity losses
Non-linear loads such as computers, LED lights, Motors etc. lead to harmonics in the electrical network. Harmonics can cause damage to the electrical components in the network. For instance, harmonic distortion can lead to transformer capacity losses by up to 5 times. By setting alerts or notifications on key PQ parameters such as harmonics, instances of poor PQ can be arrested to prevent capacity losses of the equipment. Higher harmonics also increases the kVA demand thus affecting MD billing by electric supply company.
Realizing untapped savings in energy bills
By comparing energy tariff contracts with PQ monitoring can be used to enable measures to minimize penalties due to poor Power Factor , higher MD based billing and avoid energy wastage.
CREATING A UNIFIED VIEW WITH IBMS AND PQ MONITORING
A single unified view of PQ parameters along with the conventional measurements in the IBMS provides a comprehensive analysis of the electrical network and connected equipment. By making the power related information available in a comprehensive manner the integrated system helps to detect health of system, improve the speed of response and also creates the ease in monitoring for the end users. Additionally, enabled by the comprehensive view, the teams for maintenance can correlate between the mechanical, electrical and electronic systems, observe patterns and resolve issues quickly in proactive manner rather than reactive way. On the other hand, with improved PQ, the maintenance teams can ensure greater synergy in operation of mechanical and electrical systems to bring in a significant improvement in overall energy efficiency.
CONCLUSION
Energy issues are specific to the facilities. Depending on the load, type of equipment, power quality and the operating environment, the power disturbances may vary. IBMS can be effective in addressing power issues only partially and mostly to the extent of monitoring, modification of settings, electrical network design settings, and controlling the power disturbances (for sensitive equipment). To efficiently manage the power at the facility, Operators and Facility Managers would need a greater depth of insights and controls. PQ monitoring embedded in the IBMS, shows the way. Such integrated systems enhance the IBMS’s capability to improve the reliability and safety of the electrical network, and also enable a major impact on energy efficiency. Above all, the continual PQ monitoring facility in an IBMS helps to understand and relate to equipment’s performance and response to power issues in both, within the electrical network and also in relation to other equipment.
REFERENCES
- https://www.geistglobal.com/news/company-blog/ups-failures-continue-be-top-cause-data-center-downtime
- https://www.csemag.com/articles/integrated-buildings-integrated-services-2/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330813576_An_Open_Hardware_Design_for_Internet_of_Things_Power_Quality_and_Energy_Saving_Solutions