Published On: Jul 26, 2016
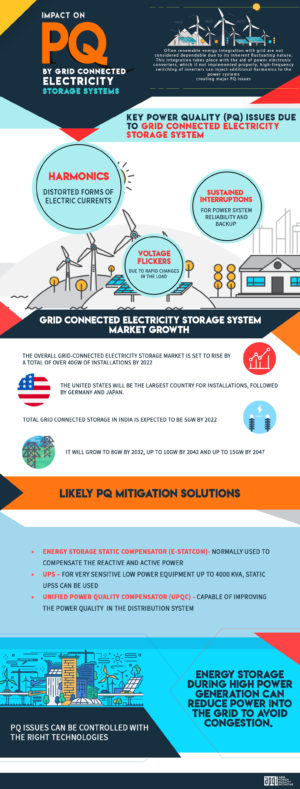
- Harmonics – Harmonics are distorted forms of electric voltages and currents that appear in the grid as a result of non-linear electric loads. This is caused by the conversion of DC to AC power by the inverter. Another factor that influences harmonic distortion in a power system is the penetration of Distributed Generation (DG) sets that uses renewable energy resources like solar PV, wind generator, etc. connected to the power system. The interaction between grid components and a group of renewable energy DG sets can amplify harmonic distortion.
|
- Voltage Flickers – Flicker is commonly seen due to rapid changes in the load or due to switching operations in the system. It is typically caused by the use of large fluctuating loads, i.e. loads that have rapidly fluctuating active and reactive power demand. Flicker effect occurs when one generating source reactive power output increases or decreases faster than the remaining generators can compensate.
POTENTIAL PQ MITIGATION SOLUTIONS
Globally, electricity storage technologies are expected to play a crucial role in grid integration and improving power quality. Utilities will have to make sure that there is good compatibility between the electrical system and the equipment. Some of the potential PQ mitigation solutions along with energy storage technologies are mentioned below:
- Energy Storage Static Compensator (E-STATCOM) is normally used by distribution utilities to compensate the reactive as well as active power, which is one of the main cause of increasing distribution system losses and various power quality issues. E-STATCOM is used for balancing source current, power factor correction, harmonic mitigation and has the capacity to maintain bus voltage sags at the required level by supplying or receiving of reactive/active power in the distribution system. (Batteries are connected in general as compared to flywheels and capacitors to the DC-side of an E-STATCOM with a DC/DC converter to control the power exchange between the storage and the interface.)
- UPS – For very sensitive low power equipment such as computers and servers, up to 4000 kVA, static UPSs can be used. There are different structures of UPSs, however, common to all structures are that active power can be supplied from an energy storage. Hence, complete mitigation of voltage dips and other power quality issues can be obtained. Depending on the size of the storage, even interruptions can be mitigated.
- The Unified Power Quality Compensator (UPQC) has compensation capabilities for the harmonic current, the reactive power compensation, the voltage disturbances, and the power flow control. However, it has no compensation capability for voltage interruption because no energy is stored. When UPQC is configured with energy storage technology connected to the DC link through the DC/DC converter, it can compensate the voltage interruption too. UPQC has the ultimate capability of improving the power quality at the installation point in the distribution system.
- Energy storage during periods of peak power generation from end-customer side can reduce the injection of renewable power into the grid to overcome voltages and congestion issues.
Broadly speaking, PQ issues often go unnoticed, but can be controlled with the right mitigating technologies coupled with energy storage technologies to avoid unpleasant surprises. Each energy storage application is unique and required careful consideration – from the selection of storage type to the system sizing, its testing, and servicing of the system.
CONCLUSION
As industry experts, facility managers know, good power quality can boost both productivity and employee safety, while poor power quality can mean a drain on the bottom line, thanks to damaged equipment, lost productivity and product spoilage. In the context of growing innovative power systems, energy storage is seen as a game changer for the power sector. The adoption of energy storage could help utilities and grid managers bring more balance to supply and demand, making the grid more resilient and efficient to be able to meet growing demand of quality power by digital age customers.
REFERENCES
- Energy Storage – Thinking Big – Russell Ray, Chief Editor, Power Engineering
- Energy Storage Solutions for Utility Scale Applications – Schneider Electric
- Grid-connected storage market set to explode – PV Magazine, 15 Jan 2014
- Voltage Flicker Mitigation using STATCOM and BESS – V.B. Virulkar and Mohan V. Aware, VNIT India
- Energy Storage equipped STATCOM for PQ improvement in Distribution Grids – Viktor Weidenmo, Sweden 2012
- Supercapacitors Energy Storage System for PQ improvement: An Overview – Kuldeep Sahay, Bharti Dwivedi, 2009
- Unified Power Quality Conditioner (UPQC) With Storage Device for Power Quality Problems – International Journal Of Engineering And Science, Sep 2013